|
|
||||||||
| Menu | Main / HomePage | |||||||
|
Downloads Installation Instructions Learning Java Documentation Tutorials Update Log Application Demos Publications People Project Roadmap Code of Conduct |
ArtiSynth: A Platform for Combined 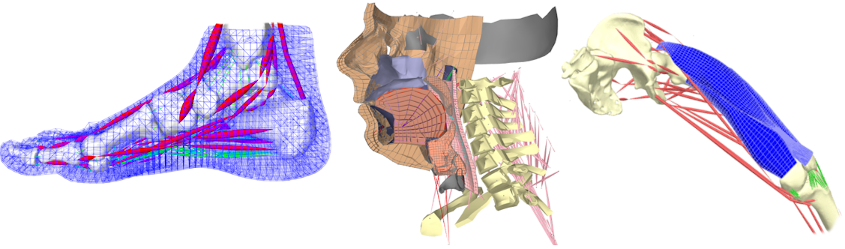 ArtiSynth is a 3D modeling platform that supports the combined simulation of multibody and finite element models, together with contact and constraints. It provides a Java-based API for model creation, together with an interactive application for model visualization, editing and simulation control. While targeted at biomechanical and biomedical applications, it can also be used for general purpose mechanical simulation. It is freely available under a two-clause BSD-style open source license. Implemented in Java, ArtiSynth provides a rich set of modeling components, including particles, rigid bodies, finite elements with both linear and nonlinear materials, point-to-point muscles, and various bilateral and unilateral constraints including contact. Models are typically assembled in Java code as a subclass of a "root model". They can then be loaded into the main application, which provides a graphical interface for component navigation, interactive property editing, some component structure editing, and simulation control. Models can also be saved to or loaded from text files with a simple JSON-like format. Full documentation is available for installation, model building, and the user interface; all documentation can be viewed on the documentation page. ArtiSynth can be downloaded either as a GitHub clone or as a precompiled release. Please acknowledge ArtiSynth if you use it: John E. Lloyd, Ian Stavness, and Sidney Fels, "ArtiSynth: A fast interactive biomechanical modeling toolkit combining multibody and finite element simulation", Soft Tissue Biomechanical Modeling for Computer Assisted Surgery, pp. 355-394, Springer, 2012. [bibtex]
The video below uses toy models to illustrate some of the system's capabilities:
ArtiSynth has been used to develop a variety of biomechanical models, including upper airway and oral structures such as the jaw, hyoid, tongue, soft palate and pharyngeal wall; a muscle activated FEM model of the face; a combined multibody/FEM model of the foot; models of the spine, arm, torso and lower limbs; and detailed FEM models of individual muscles including fiber fields and tendon sheets. It also provided the simulation platform for the OPAL and Parametric Human projects, and has been used to create airway models for use in articulatory speech synthesis. Some recent modeling work related to the design of spinal and shoulder implants, as well as the optimization of jaw reconstruction surgery, is shown below:
Other models of the cervical spine, lower limb, and jaw are seen here:
The last video shows some earlier applications, involving foot, head/neck, masseter and face models:
More details on these and other models can be found on the application demos page. Some of these are available as part of the artisynth_models package. Primary development of ArtiSynth is being undertaken by the Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering and the Department of Computer Science at the University of British Columbia. If you want to join the artisynth-updates mailing list, visit the Newsletter page; postings are made to this whenever significant new features are pushed to the GitHub repository or new precompiled releases are available.
 ArtiSynth is hosted by the Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering at the University of British Columbia. |
|||||||
| View Edit Attributes History Attach Print Search Page last modified on August 19, 2025, at 02:46 PM | ||||||||